
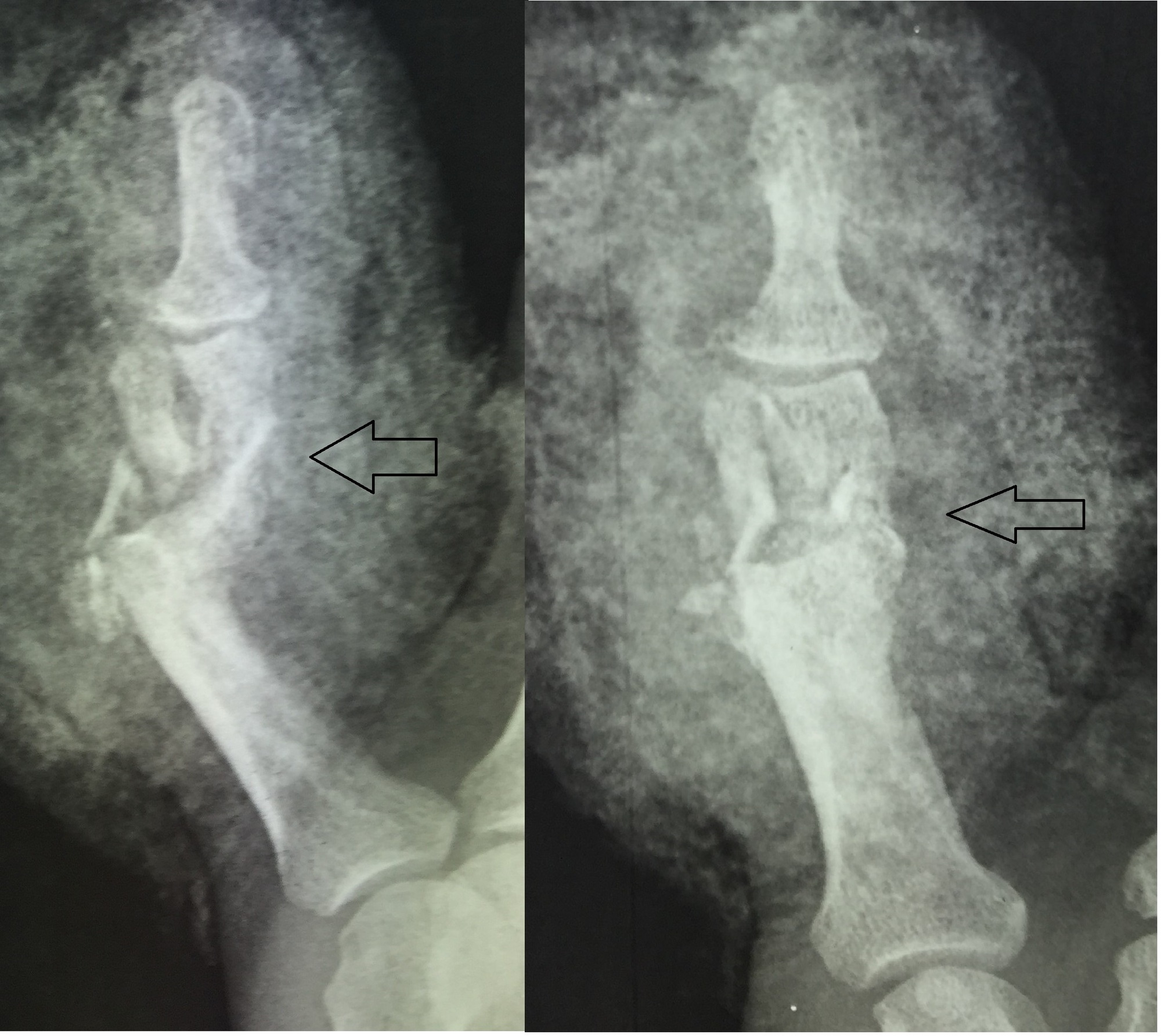
Translated: lateral movement of the bone fragments.Rotated: rotation around the longitudinal axis.Orientation : transverse, oblique, spiral.Position: diaphysis, metaphysis, epiphysis.Location: affected bone ( proximal, distal).See also “ Management of trauma patients” and “ Conservative management of fractures.” Etiologyįractures are typically classified based on the following characteristics: The specific management of different fracture types is covered in separate articles see “ Overview of common fractures” for links. Acute complications include nerve and vascular injury, hemorrhage, and acute compartment syndrome ( ACS) long-term complications include avascular necrosis and nonunion.
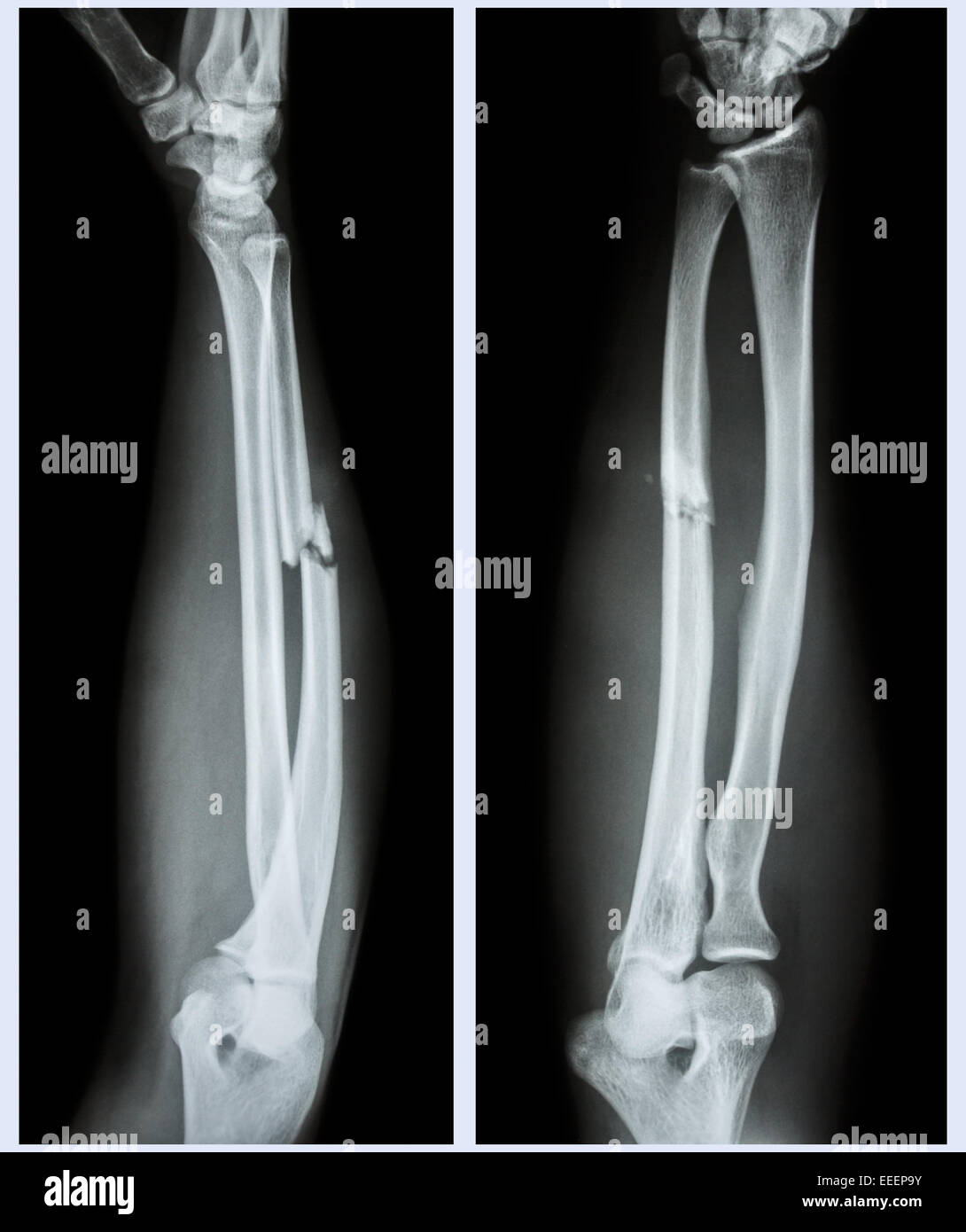
Open fractures, in which the bone is exposed due to severe soft tissue injury, require urgent surgical management and antibiotic therapy. Acute management consists of analgesia, wound care, fracture reduction, and immobilization. Fractures are typically diagnosed on x-ray CT scan and MRI are helpful adjuncts for surgical planning and diagnosis of subtle or occult fractures. Evaluation of a suspected fracture includes obtaining a patient history and assessing the skin, soft tissue, and sensory and motor function of the affected area. Fractures are named and classified according to a variety of characteristics, including location, extent, and orientation. The most common cause is trauma, followed by diseases that result in weakened bone structure. A fracture is a partial or complete interruption in the continuity of bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
